HVAC Applications: Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers for Building Comfort
HVAC Applications: Shell and Tube Heat
Exchangers for Building Comfort
What Are Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers?
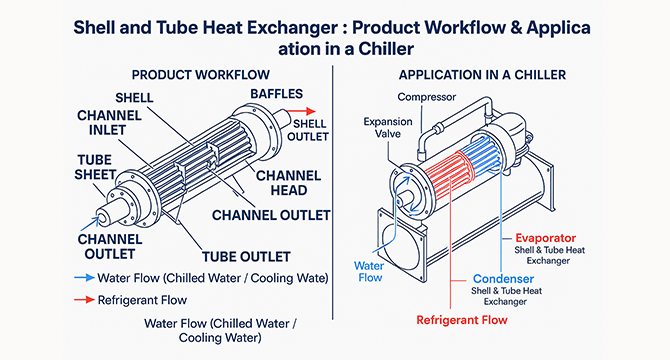
Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of a cylindrical shell. Inside, a bundle of tubes runs through it. One fluid flows through the tubes. Another flows around them in the shell. Heat transfers between fluids without mixing. This design is robust. It handles high pressures and temperatures.
In HVAC, these exchangers are common. They cool or heat air streams. For example, in air conditioners, they transfer heat between indoor and outdoor air. Their versatility suits commercial and residential setups.
Why Choose Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers for HVAC?
Efficiency matters in building comfort. Shell and tube heat exchangers excel here. They provide reliable heat transfer. High turbulence promotes better flow. This leads to energy savings.
Key advantages include:
- Durability: Built to last in demanding conditions.
- Customization: Available in various sizes and materials.
- Ease of Maintenance: Removable tube bundles simplify cleaning.
- High Pressure Handling: Ideal for large-scale HVAC systems.
Compared to plate exchangers, they resist fouling better. This reduces downtime in buildings.
Common HVAC Applications in Buildings
Chilled Water Systems
In office towers, chillers use these exchangers. They cool water for air handlers. This maintains consistent temperatures. Result: Better occupant comfort.
Hot Water Boilers
For heating, boilers employ shell and tube designs. Steam or hot water heats air. This warms spaces during winter. Efficiency cuts fuel costs.
Heat Recovery Units
Modern buildings focus on sustainability. Shell and tube heat exchangers recover waste heat. They preheat incoming air. This boosts energy efficiency.
Air Handling Units (AHUs)
AHUs condition air for distribution. Exchangers cool or heat coils. They ensure fresh, comfortable air flow.
In hotels and hospitals, these applications shine. They provide quiet, reliable operation.
Types of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers for HVAC
Variety exists in designs. Each suits specific HVAC needs.
- U-Tube Exchangers: Tubes bend in a U-shape. Easy to install. Common in institutional heating.
- Straight-Tube Fixed Tubesheet: Tubes are straight and fixed. Cost-effective for clean fluids.
- Floating Head: Allows tube expansion. Handles thermal stress in varying temperatures.
- Multi-Pass Models: Fluids pass multiple times. Increases efficiency in compact spaces.
Choose based on flow rates and space. For building HVAC, U-tube often fits best.
Design Considerations for Building Comfort
Proper design ensures peak performance. Consider these factors.
- Material Selection: Copper for high conductivity. Stainless steel for corrosion resistance.
- Size and Capacity: Match to building load. Oversizing wastes energy.
- Flow Configuration: Counterflow maximizes heat transfer.
- Pressure Drop: Minimize for efficient pumping.
- Compliance: Meet ASME standards for safety.
In LEED-certified buildings, efficient designs aid green goals.
Performance Metrics: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers | Plate Heat Exchangers | Coil Heat Exchangers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High (due to turbulence) | Very High | Moderate |
| Durability | Excellent | Good | Fair |
| Maintenance Ease | Easy (removable bundles) | Moderate | Difficult |
| Cost | Medium | Low | Low |
| Best HVAC Use | Chillers, Boilers | Compact Systems | Small Units |
| Fouling Resistance | High | Low | Medium |
Data shows shell and tube options balance cost and performance well.
Installation Tips for Optimal Comfort
Installation impacts longevity. Follow these steps.
- Site Preparation: Ensure level foundation. Allow space for maintenance.
- Piping Alignment: Avoid stress on connections.
- Insulation: Prevent heat loss. Boost efficiency.
- Testing: Hydro-test per ASME. Check for leaks.
In retrofits, integrate with existing ducts. This minimizes disruption.
Maintenance Best Practices
Regular upkeep keeps systems running. Shell and tube heat exchangers need attention.
Inspect tubes quarterly. Clean to remove scale. Use chemical treatments if needed.
Monitor pressure drops. High drops signal fouling. Address promptly.
Replace gaskets annually. This prevents leaks.
In humid climates, corrosion checks are crucial. Extend lifespan with coatings.
Proper maintenance ensures consistent building comfort.
Case Studies: Real-World Success
Consider a high-rise office in a certain location. They installed shell and tube heat exchangers in their chiller plant. Result: 15% energy savings. Occupants reported better comfort.
A hospital in a certain location upgraded boilers. New exchangers reduced heating times. Improved patient environments.
These examples highlight reliability in diverse settings.
Future Trends in HVAC Heat Exchange
Innovation drives the field. Shell and tube heat exchangers evolve.
Smart sensors monitor performance. IoT integration predicts failures.
Eco-friendly materials reduce environmental impact.
Hybrid designs combine with renewables. Think solar-assisted HVAC.
These trends promise greener, more comfortable buildings.
Conclusion: Elevate Building Comfort Today
Shell and tube heat exchangers are essential for HVAC. They deliver efficient, reliable heat transfer. From chillers to heat recovery, they enhance comfort.
Invest in quality designs. Enjoy lower costs and better performance.
Ready to upgrade? Consult experts for tailored solutions.


